ASTM A672 is a steel pipe made from a pressure vessel quality plate, Electric-Fusion-Welded (EFW) for high-pressure service at moderate temperatures.
Navigation Buttons
ASTM A672 Grade Classification
ASTM A672 Class Classification
ASTM A672 Size Range
Welding Precautions
Heat Treatment
Chemical Components
Tension Test
Transverse-Guided-Weld-Bend Tests
Pressure Test
Radiographic Examination
Dimensional tolerances for ASTM A672
ASTM A672 Appearance
Defects and Repair
ASTM A672 Marking
Application of ASTM A672 Steel Pipe
Our Related Products
ASTM A672 Grade Classification
Classified according to the type of plate used to manufacture steel tubes.
Different grades represent different chemical compositions and mechanical properties for different pressure and temperature conditions.
| Pipe Grade | Type of Steel | ASTM Specification | |
| No. | Grade | ||
| A 45 | plain carbon | A285 / A285M | A |
| A50 | plain carbon | A285 / A285M | B |
| A 55 | plain carbon | A285 / A285M | C |
| B 60 | plain carbon, killed | A515 / A515M | 60 |
| B 65 | plain carbon, killed | A515 / A515M | 65 |
| B 70 | plain carbon, killed | A515 / A515M | 70 |
| C 55 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516 / A516M | 55 |
| C 60 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516 / A516M | 60 |
| C 65 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516 / A516M | 65 |
| C 70 | plain carbon, killed, fine grain | A516 / A516M | 70 |
| D 70 | manganese-silicon, normalized | A537 / A537M | 1 |
| D 80 | manganese-silicon, Q&TA | A537 / A537M | 2 |
| H 75 | manganese-molybdenum, normalized | A302 / A302M | A |
| H 80 | manganese-molybdenum, normalized | A302 / A302M | B, C, or D |
| J 80 | manganese-molybdenum, Q&TA | A533 / A533M | Cl-1B |
| J 90 | manganese-molybdenum, Q&TA | A533 / A533M | Cl-2B |
| J 100 | manganese-molybdenum, Q&TA | A533 / A533M | Cl-3B |
| L 65 | molybdenum | A204 / A204M | A |
| L 70 | molybdenum | A204 / A204M | B |
| L 75 | molybdenum | A204 / A204M | C |
| N 75 | manganese-silicon | A299 / A299M | A |
A Q&T = quenched and tempered.
В Any grade may be furnished.
We can initially determine the type of steel pipe by the letters in the grade.
Grades beginning with the letters A, B, and C usually indicate carbon steel pipe.
Grades beginning with the letters D, H, J, L, and N indicate alloy steel pipe.
ASTM A672 Class Classification
The tubes are classified according to the type of heat treatment they receive during the manufacturing process and whether or not they are radiographically inspected and pressure tested.
| Class | Heat treatment on pipe | Radiography, see note: | Pressure test, see note: |
| 10 | none | none | none |
| 11 | none | 9 | none |
| 12 | none | 9 | 8.3 |
| 13 | none | none | 8.3 |
| 20 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | none | none |
| 21 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | 9 | none |
| 22 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 23 | stress relieved, see 5.3.1 | none | 8.3 |
| 30 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | none | none |
| 31 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | 9 | none |
| 32 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 33 | normalized, see 5.3.2 | none | 8.3 |
| 40 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | none | none |
| 41 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | 9 | none |
| 42 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 43 | normalized and tempered, see 5.3.3 | none | 8.3 |
| 50 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | none | none |
| 51 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | 9 | none |
| 52 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | 9 | 8.3 |
| 53 | quenched and tempered, see 5.3.4 | none | 8.3 |
Special attention should be paid to the expected service temperature when selecting the appropriate material class. Refer to specification ASTM A20/A20M.
ASTM A672 Size Range
Recommended size ranges:DN≥400mm[16 in] and WT≤75mm[3 in].
For other sizes of pipe, provided it meets all other requirements of this specification, it may also be used.
Welding Precautions
Seams shall be double-welded, full-penetration welded.
The welds shall be made either manually or automatically by an electric process involving the deposition of filler metal.
Welds may be inspected using radiography and should follow the provisions in Section VII UW-51 of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
The height of the weld shall not exceed 3 mm [1/8 in].
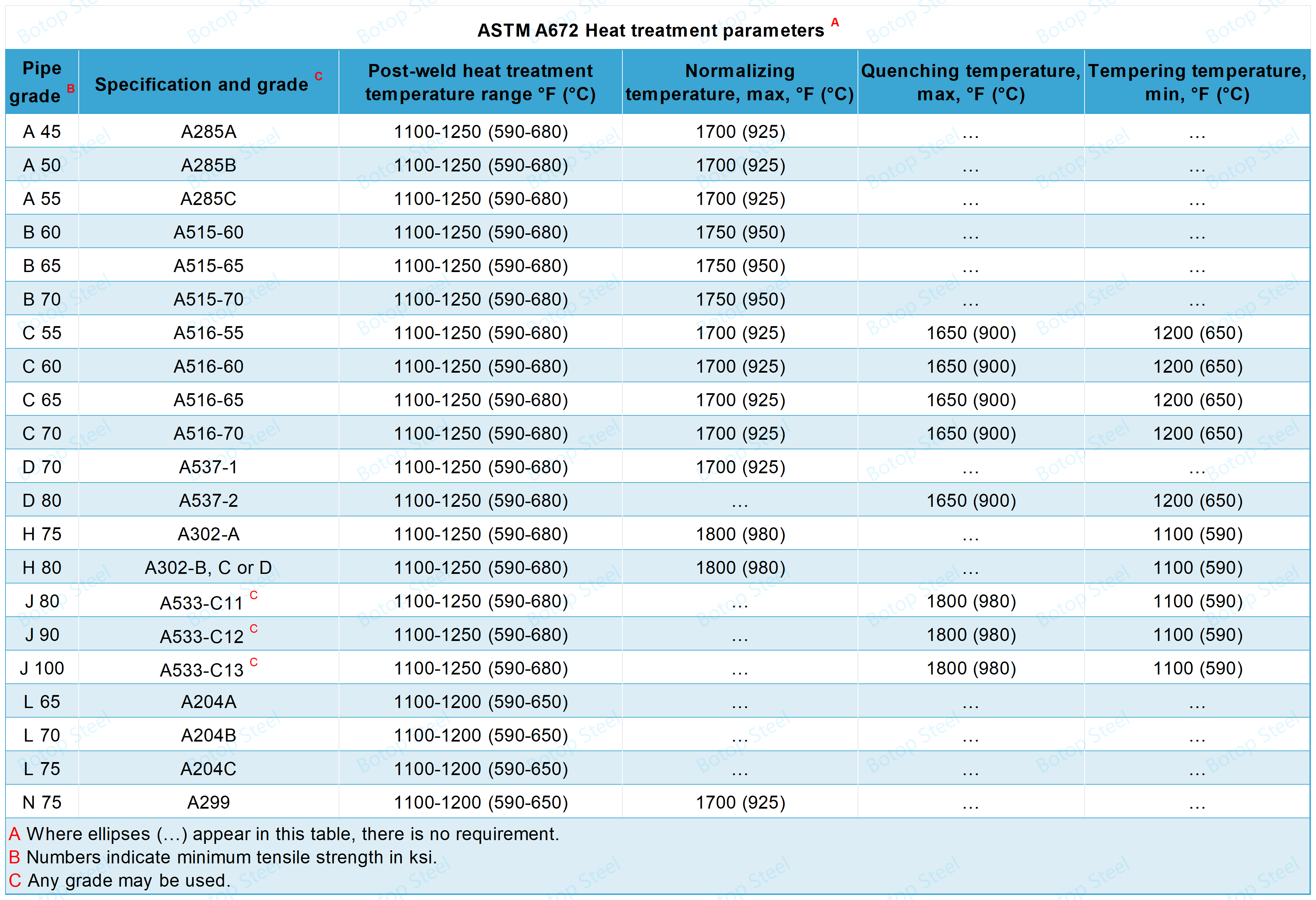
Heat Treatment
All classes other than 10, 11, 12, and13 shall be heat treated in furnace controlled to ±25 °F[± 15°C]:
Classes 20, 21, 22, and 23
The pipe shall be uniformly heated within the post-weld heat-treatment temperature range indicated in Table 2 for a minimum of 1 h/in. [0.4 h/cm] of thickness or for 1 h, whichever is greater.
Classes 30, 31, 32, and 33
The pipe shall be uniformly heated to a temperature in the austenitizing range and not exceeding the maximum normalizing temperature indicated in Table 2 and subsequently cooled in the air at room temperature.
Classes 40, 41, 42, and 43
The pipe shall be normalized.
The pipe shall be reheated to the tempering temperature indicated in Table 2 as a minimum and held at a temperature for a minimum of 0.5 h/in.[0.2 h/cm] of thickness or for 1/2 h, whichever is greater, and air-cooled.
Classes 50, 51, 52, and 53
The pipe shall be uniformly heated to temperatures within the austenitizing range and not exceeding the maximum quenching temperatures shown in Table 2.
Subsequently, quench in water or oil. After quenching, the pipe shall be reheated to the minimum tempering temperature shown in Table 2 and held at that.
temperature for a minimum of 0.5 h/inch [0.2 h/cm] of thickness or 0.5 h, whichever is greater, and air-cooled.
Chemical Components
It shall be the responsibility of the manufacturer to test the chemical composition of the plate and welds for compliance with the requirements of the plate specification for the material ordered and the welding procedure for depositing the weld metal, respectively.
Tension Test
Experimental frequency: one specimen per lot.
Test Method: Test specimens shall be made in accordance with QW-150 in Section IX of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code. Specimens shall be tested at room temperature in accordance with Test Methods and Definition A370.
In addition for Grades Dxx, Hxx, Jxx, and Nxx in Classes 3x, 4x, and 5x transverse tensile properties of the base plate, shall be determined on specimens cut from the heat-treated pipe.
Requirements for results: Transverse tensile properties of the welded joint shall meet the minimum requirements for the ultimate tensile strength of the specified plate material.
Transverse-Guided-Weld-Bend Tests
Number of Tests: Experimental frequency: once per batch, two specimens
Experimental method: The test requirements of Test Methods and Definitions A370, paragraph A2.5.1.7 shall be met.
For wall thickness over 3/ 8 in. [10 mm] but less than 3/4 in. [19 mm] Side-bend tests may be made instead of the face and root-bend tests.
For wall thicknesses 3/4 in. [19 mm] and over both specimens shall be subjected to the side-bend test.
Requirements for results: The bend test shall be acceptable if no cracks or other defects exceeding 1/8 in. [3 mm] in any direction are present in the weld metal or between the weld and the base metal after bending.
Cracks that originate along the edges of the specimen during testing, and that are less than 1/4 in. [6 mm] measured in any direction shall not be considered.
Pressure Test
Classes X2 and X3 pipe shall be tested in accordance with Specification A530/A530M, Hydrostatic Test Requirements.
Radiographic Examination
The full length of each weld of Classes X1 and X2 shall be radiographically examined in accordance with and meet the requirements of ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII, Paragraph UW-51.
The radiographic examination may be performed prior to heat treatment.
Dimensional tolerances for ASTM A672
| Sports | Tolerance Value | Note |
| Outside Diameter | ±0.5% | Based on the circumferential measurement |
| Out-of-Roundness | 1%. | Difference between major and minor outside diameters |
| Alignment | 1/8 in. [3 mm] | Using a 10 ft [3 m] straight edge placed so that both ends are in contact with the pipe |
| Thickness | 0.01 in. [0.3 mm] | Minimum wall thickness less than the specified nominal thickness |
| Lengths | 0-+0.5in [0-+13mm] | unmachined ends |
ASTM A672 Appearance
The finished pipe shall be free of injurious defects and shall have a workmanlike finish.
The same requirements as in specification ASTM A20/A20M for surface finish of steel plates.
Defects and Repair
Defect Determination
The ASTM A672 standard does not specify acceptable levels of defects and determination criteria for piping and usually refers to relevant engineering standards and industry practices.
Internal defects: Internal defects may include porosity, slag, inclusions, etc.
External defects: External defects may include cracks, dents, scratches, etc.
Removal by Regrinding
Surface defects can be removed by overgrinding or machining with a residual thickness of not less than 0.3 mm below the standard thickness.
The regrind depression should be uniformly blended into the surrounding surface.
Welding Repair
Defects shall be removed by suitable mechanical or thermal cutting or dicing methods and prepared to repair welded cavities.
and radiologically examined in accordance with the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII, Paragraph UW-51.
The full length of the repaired pipe shall be heat-treated after repair in accordance with the specified piping grade requirements.
ASTM A672 Marking
The marking is to contain the following:
Manufacturer's identifier, such as a trademark or logo.
Specification of the pipe (size, wall thickness, etc.).
Material grade or type of pipe. Example: C60-22 (abbreviation for grade: C60 and class 22).
The manufacturing standard of the pipe is ASTM A672.
Production date or production lot number.
Application of ASTM A672 Steel Pipe
In the electric power industry, ASTM A672 Electric Welded Steel Pipe is commonly used to convey steam in boiler systems.
In the chemical industry, ASTM A672 welded steel pipe is usually used to transport various chemicals, acid, and alkali solutions, and other media.
In the oil and gas industry, ASTM A672 welded steel pipe is commonly used to transport crude oil, natural gas, and other liquids or gases.


We are a high-quality welded carbon steel pipe manufacturer and supplier from China, and also a seamless steel pipe stockist, offering you a wide range of steel pipe solutions!
Tags: ASTM a672, efw, carbon steel pipe, grade.
Post time: Apr-23-2024

